Managing field sales teams requires confidence that store visits are genuine and executed at the correct locations. When sales representatives operate across multiple territories, verifying whether a visit actually happened at the assigned store becomes critical.
GPS validation helps organizations ensure authentic store visits, eliminate false reporting, and improve execution accuracy using location-based validation.
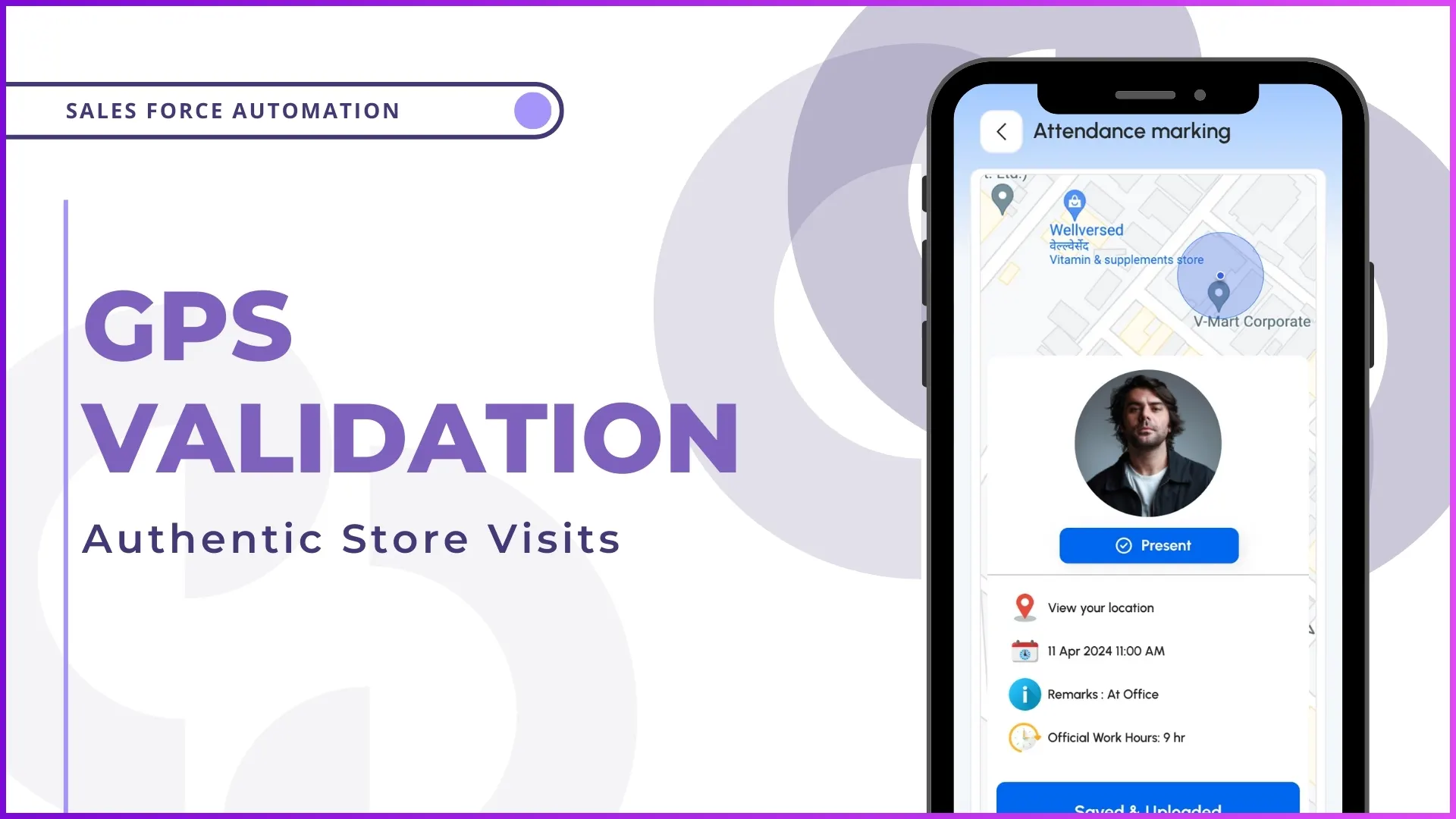
What Is GPS Validation in Store Visits?
GPS validation is a mechanism that verifies a field employee's physical presence at a store using real-time location coordinates captured through a field sales application.
Every store is mapped with predefined GPS coordinates, and visits are validated by matching the employee's location with the store's registered location.
Example:
A sales representative marks a visit to a retail outlet. The system checks whether the employee's GPS location falls within the defined range of that store before confirming the visit as valid.
Why GPS Validation Is Essential for Field Sales Teams
Without location validation, store visits may be logged without actual physical presence, leading to inaccurate reporting and poor field execution visibility. GPS validation ensures that every reported visit reflects real on-ground activity.
Example:
If a sales executive attempts to mark a visit while standing far from the assigned outlet, the system flags or restricts the action, ensuring visit authenticity.
How GPS Validation Works for Store Visits
GPS validation works by combining store master data and real-time employee location tracking. Each store is mapped with latitude and longitude details, and visits are allowed only when the employee is within the permitted radius.
Key Working Flow:
- Store GPS coordinates are pre-configured in the system
- Employee location is captured at the time of visit
- Distance between employee location and store location is validated
- Visit is accepted or rejected based on location accuracy
Example:
A distributor store is mapped in the system. When the salesperson reaches the store and checks in, the GPS location confirms proximity and validates the visit automatically.
Preventing Fake or Proxy Store Visits
GPS validation prevents employees from marking visits remotely or on behalf of others. This ensures visit data reflects actual market activity rather than manual or assumed entries.
Example:
A sales rep trying to mark multiple store visits from one location will fail GPS validation for stores that are not physically nearby.
Ensuring Visit Compliance and Discipline
With GPS validation in place, organizations can enforce discipline by ensuring visits are carried out as per assigned routes and schedules. This leads to better adherence to daily field plans.
Example:
If a salesperson skips a planned outlet and tries to mark the visit later from another location, the system identifies the mismatch and records the visit as invalid.
Ensure authentic store visits with GPS validation
Strengthen field execution control and eliminate fake visits with 1Channel SFA.
Explore Sales Force AutomationImproving Accuracy of Store-Level Reporting
Validated visits improve the accuracy of reports related to coverage, productivity, and execution. Since each visit is location-verified, management can rely on the data for performance analysis.
Example:
Reports showing completed store visits reflect only GPS-validated visits, helping managers assess actual market coverage rather than assumed activity.
Supporting Audit and Performance Reviews
GPS-validated visit data provides a reliable audit trail. Organizations can review visit histories with confidence during audits or performance evaluations.
Example:
During a monthly review, managers can track which stores were genuinely visited, along with time and location details captured during each visit.
Reducing Manual Errors and Disputes
Manual visit entries often lead to discrepancies and disputes between field teams and managers. GPS validation removes ambiguity by providing objective location-based proof.
Example:
If a visit is questioned, GPS data confirms whether the employee was present at the store location at the reported time.
GPS Validation as Part of Field Execution Control
GPS validation integrates seamlessly into daily field workflows, ensuring that visit tracking becomes a natural part of execution rather than an additional task.
Example:
Sales representatives simply check in at the store, and validation happens automatically in the background without manual intervention.
GPS Validation in 1Channel SFA Software
1Channel SFA software includes GPS validation to ensure store visits are authentic and accurately recorded. By validating employee location against registered store coordinates, it helps organizations maintain reliable field data, enforce visit discipline, and improve execution transparency across sales operations.

