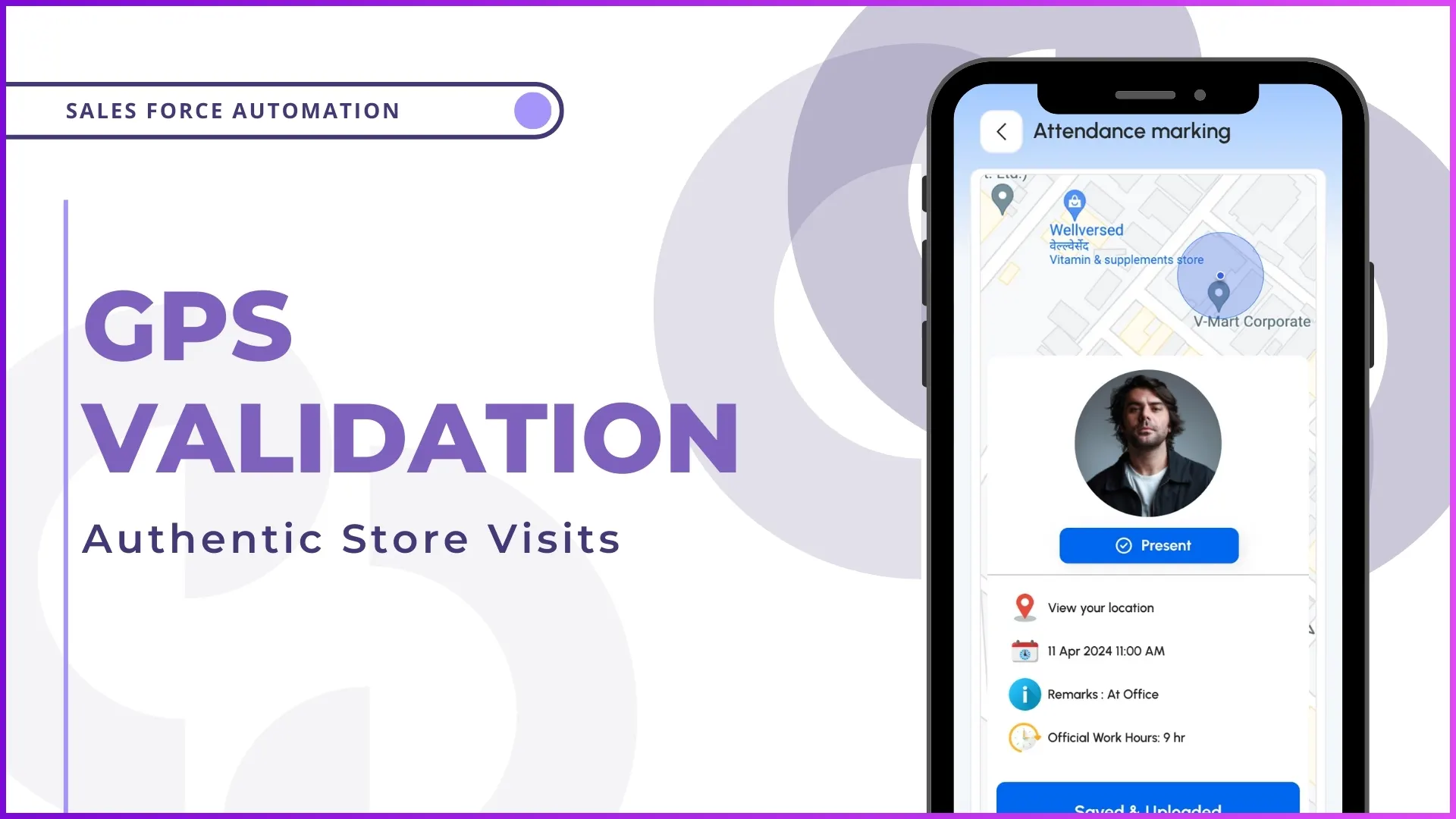
Beat planning is a critical activity for organizations managing field sales and on-ground teams. It ensures that every market, route, and outlet is covered in a planned and organized manner. When beat planning is executed systematically, it brings clarity to daily field execution and helps teams avoid random or overlapping market visits.
This blog explains beat planning, its role in structured market coverage, and how it supports disciplined field execution using examples derived from the provided content.

What Is Beat Planning?
Beat planning refers to the process of defining which markets, routes, or outlets a field executive should visit on specific days. A beat acts as a predefined path or coverage plan that guides sales representatives on where they need to go and what they need to cover.
Instead of allowing field staff to decide their daily visits on the spot, beat planning provides a clear framework that aligns daily movement with business priorities.
Example:
A sales representative is assigned a fixed beat for Mondays that includes Market A and Market B. Every Monday, the representative follows the same beat, ensuring consistent coverage of those markets.
Why Beat Planning Is Essential for Market Coverage
Without beat planning, field activities often become inconsistent. Some markets may be visited repeatedly, while others may be ignored entirely. Beat planning introduces structure and balance into field operations.
Key benefits highlighted in the content include:
- Planned coverage of assigned markets
- Reduced chances of missed or duplicate visits
- Clear expectations for field teams
Example:
If a region has 40 outlets and no beat plan, a sales executive might focus only on familiar stores. With beat planning, all 40 outlets are distributed across weekdays, ensuring none are skipped.
Beat Planning as Part of Market Visit Planning
Beat planning works closely with market visit planning. The document explains how visits can be planned day-wise and store-wise, helping managers define exact coverage expectations.
Using a beat plan, managers can:
- Assign specific markets to specific days
- Control how many stores are visited per day
- Ensure workload balance across the week
Example:
A weekly plan assigns:
- Monday: 10 stores in Market North
- Tuesday: 8 stores in Market East
- Wednesday: 12 stores in Market South
This structure prevents overcrowding of visits on a single day.
Day-Wise Beat Allocation for Field Teams
The content emphasizes day-wise planning as a core component of beat execution. Field executives receive a clear daily roadmap, reducing confusion and dependency on ad-hoc decisions.
Day-wise beat allocation helps in:
- Better time management
- Predictable daily schedules
- Consistent execution across teams
Example:
A field executive knows in advance that Thursdays are reserved for rural market visits, while Fridays are for urban retail outlets. This predictability improves preparedness and efficiency.
Streamline field execution with beat planning
Plan day-wise market coverage and track execution with 1Channel workforce management software.
Explore Workforce Management SoftwareApproval-Based Beat Planning for Better Control
The document highlights the importance of approval workflows in market and beat planning. Beat plans can be reviewed and approved by managers before execution, ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
This approval process:
- Prevents unrealistic planning
- Aligns field activity with sales priorities
- Adds accountability to planning
Example:
A sales executive submits a weekly beat plan. The manager reviews the number of stores planned per day and approves it only after ensuring coverage is evenly distributed.
Beat Planning and Actual Visit Tracking
Beat planning is not just about planning—it also supports comparison between planned visits and actual visits. Managers can review execution accuracy and identify deviations.
This comparison helps in:
- Measuring adherence to plans
- Identifying skipped or extra visits
- Improving future beat planning
Example:
A plan shows 10 scheduled visits for Wednesday, but only 7 were completed. Managers can analyze the gap and take corrective action.
Reducing Market Overlaps with Beat Planning
One of the challenges in field operations is overlapping coverage by multiple executives. Beat planning minimizes this by clearly defining territories and visit schedules.
Example:
Two sales executives working in the same city are assigned different beats. One covers central markets, while the other handles suburban outlets, avoiding duplication.
Improving Productivity Through Structured Beats
The document explains that structured beat planning directly improves field productivity. When routes and visits are predefined, executives spend less time deciding where to go and more time executing tasks.
Example:
Instead of spending the first hour of the day deciding which stores to visit, the executive follows the predefined beat and starts execution immediately.
Role of Beat Planning in Performance Review
Beat plans provide a reference point for performance evaluation. Managers can assess whether field staff followed assigned routes and completed planned visits.
This supports:
- Objective performance tracking
- Data-backed reviews
- Transparent accountability
Example:
A manager reviews weekly reports to see how closely actual visits matched the beat plan, rather than relying on verbal updates.
Ready to optimize field market coverage?
Implement beat planning and structured visit tracking with 1Channel SFA.
Explore Sales Force AutomationFAQs
What is the main purpose of beat planning?
Beat planning ensures structured, consistent, and complete market coverage by defining routes and visit schedules in advance.
How does beat planning help managers?
It gives managers visibility into planned coverage, enables approval control, and helps track execution against plans.
Is beat planning done daily or weekly?
Based on the document, beat planning is typically done in advance, often on a weekly basis, with day-wise allocation of markets and stores.
Can beat planning reduce missed market visits?
Yes. By distributing outlets across days and routes, beat planning significantly reduces the risk of missed visits.
How is beat planning linked to execution tracking?
Planned beats are compared with actual visits, allowing managers to measure adherence and improve future planning.